What Is KM?
Knowledge Management (KM) involves the people, processes, content, culture, and enabling technologies—necessary to Capture, Manage, Share, and Find information.
Our definition of Knowledge Management is purposely broad to ensure it covers everything necessary for an organization to be truly successful in designing, implementing, and maintaining a Knowledge Management program that adds real business value.
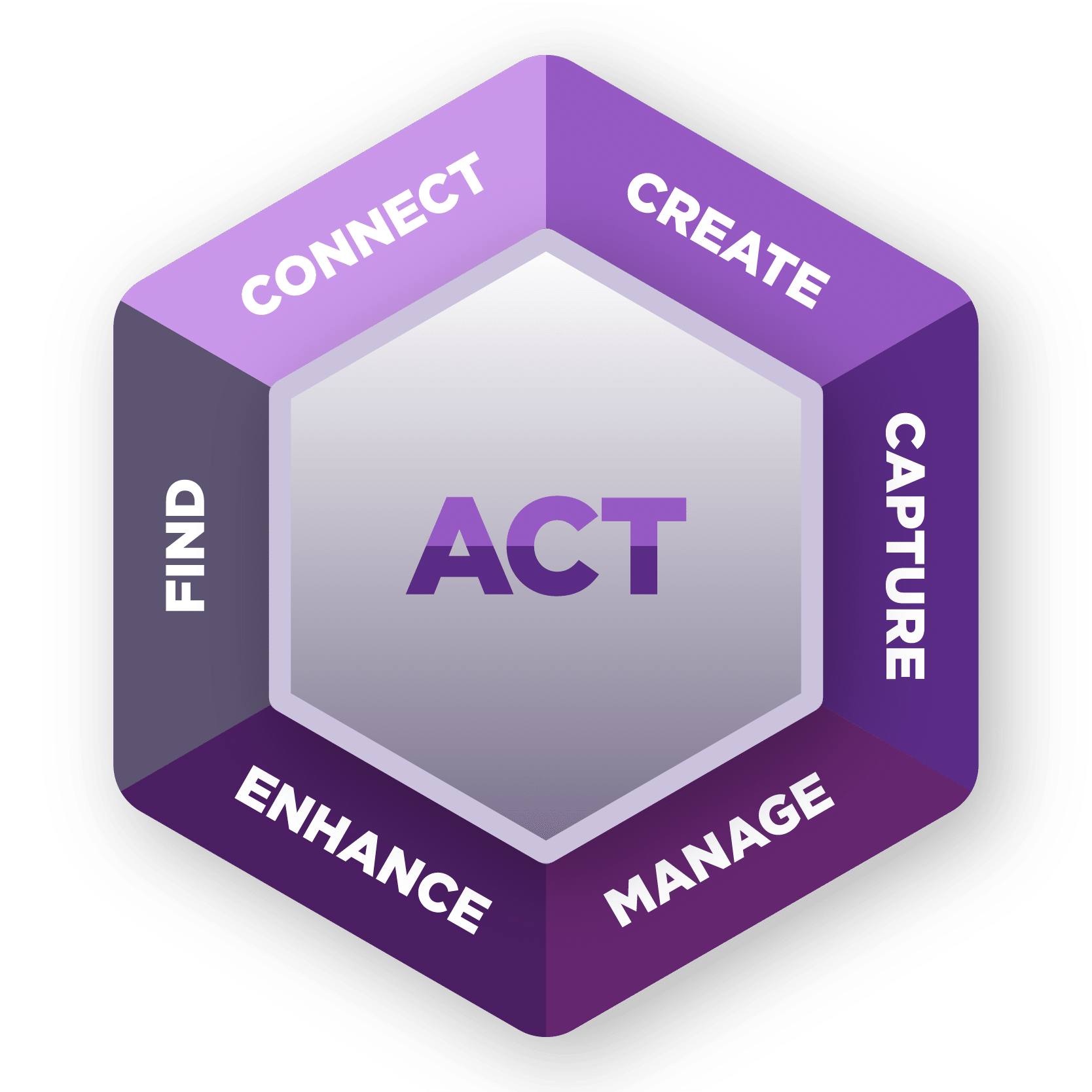
Simply put, effective Knowledge Management is about enabling organizations and the individuals within and between them to take actions: to do things that will help their knowledge last within the organization, be shared, and therefore be leveraged by others. We want them to be able to capture their knowledge in reusable forms, manage it so it is consistently reliable and improving, share it so others may benefit from it, and find it so we can further act upon it.
We further explain this process using our KM Action Wheel.
The 5 Elements of KM
The other key component to our definition is the KM elements. The 5 KM elements are People, Process, Content, Culture, and Technology.
People refers to the individuals who hold the knowledge, the individuals who need knowledge to grow and perform, and the flow of knowledge between the two groups.
Process refers to the policies and procedures, roles, and responsibilities governing the capture, management, and maintenance of knowledge and information.
Content refers to the full breadth of an organization’s knowledge, information, and data in any form: tacit and explicit, structured and unstructured.
Culture refers both to an organization’s leadership supporting good KM practices and the overall willingness of individuals within it to share their knowledge.
Technology refers to the KM systems themselves: what they are, how well they are designed, how they are operated and maintained, and the extent to which they are aligned and integrated with each other.
We approach KM from a balanced perspective, considering all five of these elements necessary for success, as minimizing any of the five may put an entire KM initiative at risk.
The Value of KM
There are two ways to talk about KM value: KM Outcomes and Business Outcomes. KM Outcomes are the result of KM transformations and the successful implementation of KM systems, while Business Outcomes reflect the complete return on the initial KM investment within 2-3 years of commencing the transformation. The following are the most common, meaningful, and easily measured KM and Business Outcomes:
KM Outcomes
- Improved content findability and discoverability, and therefore less time waiting, searching, and recreating knowledge
- Increased use and reuse of information
- Decreased knowledge loss
- Improved organizational awareness and alignment
- Enhanced quality, availability, and speed of learning
Business Outcomes
- Improved productivity
- Decreased costs (and cost avoidance)
- Increased employee satisfaction and retention
- Faster and better upscaling of employees
- Improved customer satisfaction and retention
- Improved delivery and sales
- Increased collaboration and innovation
- Future readiness
Ready to get KM working for your company?
